TRADING
ELECTRICITY MARKET
Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market
The Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market in electricity operated by PolPX offers short-term electricity buy and sell transactions (spot market).
The Day-Ahead Market opened in June 2000 and is a physical spot market in electricity. This PolPX market lists hourly instruments for each hour of delivery day (24 instruments). It also lists three block instruments (BASE – delivery of 1 MWh in each hour of the day, PEAK – delivery of 1 MWh in each peak hour, i.e., from 07:00 to 22:00, and OFFPEAK – delivery of 1 MWh from 00:00 to 07:00 and from 22:00 to 24:00). Trade on the Day-Ahead Market takes place two days before and one day before the day of delivery. Trade on the Intra-Day Market takes place one day before the day of delivery and on the day of delivery.
In 2014, the volume of trade in electricity on the Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market was 23.7 TWh. The year-on-year increase (from 22.3 TWh in 2013) was mainly driven by higher energy consumption in Poland in 2014, higher volatility of prices on the PSE Balancing Market, and changes to the Day-Ahead Market trading schedule which reduced the number of domestic fixings from two to one.
Volume of trade in electricity on the Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market (TWh)
The Commodity Forward Instruments Market in electricity opened on PolX in November 2008 and offers trade in standard forward instruments for delivery of the same quantity of electricity on every hour of delivery. Contracts are executed on a weekly, monthly, quarterly and annual basis. The Commodity Forward Instruments Market lists the following types of contracts: BASE with delivery in each hour of the day, PEAK5 with delivery from 07:00 to 22:00 on business days, and OFFPEAK with delivery from 00:00 to 07:00 and from 22:00 to 24:00 on business days and from 00:00 to 24:00 on holidays.
The volume of trading in electricity on the commodity forward market was 163.0 TWh in 2014. The year-on-year increase of the volume was due to the higher electricity consumption in Poland in 2014, higher volatility of prices on the PolPX Day-Ahead Market and higher liquidity of the market after PolPX signed additional market maker agreements.
Volume of trade in electricity on the Commodity Forward Instruments Market (TWh)
GAS MARKET
Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market in Gas
On 31 December 2012, PolPX launched a spot market in natural gas and opened trade on the Day-Ahead Market in gas. The Day-Ahead Market in gas lists the following types of contracts: BASE with delivery on 24 hours of the next day of the same quantity of gas in every hour of the day, and WEEKEND with delivery on two days (Saturday and Sunday) of the same quantity of gas in every hour of the day (between 47 and 49 hours).
On 30 July 2014, PolPX launched the Intra-Day Market in gas. The Intra-Day Market in gas lists hourly instruments with delivery on the day of trading.
In 2014, the number of entities authorised for operation on the Day-Ahead and Intra-Day Market in gas increased and instruments with delivery over the weekend were introduced to trading. The volume of trading was supported by a change of the trading schedule on the Day-Ahead Market in gas which added an opening fixing and extended trading for another 30 minutes.
Volume of trade in natural gas on the Day-Ahead Market (TWh)
Commodity Forward Instruments Market in Gas
Since 20 December 2012, PolPX offers trade in forward instruments with physical delivery of natural gas on the Commodity Forward Instruments Market. It offers trade in standard forward products for delivery of natural gas in the same quantity in the exercise hours on a weekly, monthly, quarterly, seasonal and annual basis. Trade is available in BASE contracts with delivery of gas on 24 hours of the day.
Volume of trade in natural gas on the Commodity Forward Instruments Market (TWh)
Property Rights Market
PolPX operates a Property Rights Market (PRM) in certificates of origin of electricity produced:
- from renewable energy sources (PMOZE and PMOZE_A, known as green certificates),
- in high-efficiency cogeneration (PMGM, known as yellow certificates; PMEC, known as red certificates; and PMMET, known as purple certificates).
Moreover, the following instruments can be traded on PRM:
- property rights in certificates of origin of biogas (PMBG, known as brown certificates), and
- property rights in energy efficiency certificates (PMEF, known as white certificates).
The Property Rights Market is the foundation of Poland’s support system for producers of energy from renewable energy sources. It allows producers of energy from renewable energy sources, cogeneration, biogas and holders of energy efficiency certificates to sell property rights, and energy operators required to pay substitution fees or to cancel certificates of origin to meet that obligation.
The volume of trading on the Property Rights Market is driven by the number of certificates issued in the Register of Certificates of Origin: increased production of energy generates the obligation to issue more certificates of origin, which in turn generates an increase of the volume of certificates of origin available on the market.
In 2014, the volume of trading in property rights in certificates of origin of electricity generated from renewable energy sources was 32.1 TWh, an increase of 47% year on year as a result of increased production of energy from renewable sources.
Volume of trade in property rights in renewable energy sources (TWh)
The volume of trading in certificates of origin of energy from cogeneration,[1] i.e., red and yellow certificates, in 2014 was 2.5 TWh (a decrease of 82% year on year) and 0.6 TWh (a decrease of 81%), respectively. The dramatic decrease in trading was mainly driven by changes in the legal environment of the energy industry.
The statutory support system for producers of energy from high-efficiency cogeneration (PMEC and PMGM) expired at the end of March 2013. The vast majority of transactions in 2013 took place in Q1 in keeping with the obligation for 2012, the last full year of the statutory obligation. The obligation to cancel certificates of origin of energy produced in high-efficiency cogeneration was reinstated in 2014 and the first transactions in the resumed system took place in late July 2014.
[1] Cogeneration – technological process where electricity and heat are generated simultaneously in a combined heat and power plant. Thanks to lower consumption of fuel, cogeneration provides material economic benefits and environmental advantages over separate generation of heat in a traditional heat plant and of electricity in a condensation power plant.
Volume of trade in cogeneration property rights (TWh)
Purple certificates of origin of energy (PMMET) are issued for energy produced in units fired with methane gas released and sequestered in mine work in coal mines that are active, are under liquidation or have been liquidated, as well as gas from processing of biomass. It is the smallest cogeneration segment which has been growing steadily year after year (year-on-year increase by 33% from 0.6 TWh to 0.8 TWh).
The first-ever transaction in energy efficiency certificates (PMEF) took place in 2014.
REGISTER OF CERTIFICATES OF ORIGIN
The Register of Certificates of Origin is a system of registration and recording of certificates of origin which confirm that electricity was generated in high-efficiency cogeneration or from renewable energy sources or confirm that agricultural biogas was produced and introduced to the gas distribution network, as well as energy efficiency certificates which confirm that the project improved energy efficiency, and recording of property rights under such certificates. A certificate of origin of energy confirms that electricity was generated in high-efficiency cogeneration or from renewable energy sources or that agricultural biogas was produced and introduced to the gas distribution network. An energy efficiency certificate issued by the President of the Energy Regulatory Office confirms that the project improved energy efficiency.
The main functions of the Register of Certificates of Origin include:
- to identify entities entitled to property rights in certificates of origin,
- to identify property rights under certificates of origin and the corresponding quantity of electricity,
- to register certificates of origin and the resulting property rights,
- to record transactions in property rights and balances of property rights in certificates of origin,
- to issue documents confirming property right balances in the register, used by the Energy Regulatory Office for cancellation of certificates of origin.
Certificates Issued and Cancelled (Register of Certificates of Origin)
In 2014, members of the Register of Certificates of Origin received into their registration accounts 42.3 bn property rights in certificates of origin of all types (1 property right represents 1 kWh of electricity under certificates of origin), compared to 29.4 bn in 2013. In 2014, entities required to cancel certificates of origin cancelled 20.6 bn property rights in certificates of origin, compared to 36.2 bn in 2013.
In 2014, the number of issued and cancelled certificates of origin of energy from renewable energy sources increased sharply (certificates issued by 82% year on year from 11.9 TWh in 2013 to 21.6 TWh in 2014, certificates cancelled by 127% from 8.8 TWh to 20.8 TWh). The growth rate was driven among others by the draft Renewable Energy Sources Act, which is disadvantageous to the renewable energy industry and provides than certain energy producers will be excluded from the existing support system. In order to remain in the old support system based on certificates of origin, investors must complete their investment projects by the end of 2015, which in turn generates an above-average number of green certificates issued in the Register of Certificates of Origin.
Cancellation of certificates for a given calendar year ends in the first quarter of the next year. In practice, nearly one half of all cancellations are uploaded to the system within the original year of the obligation and the remainder in the first quarter of the following year. The 2013 cancellations were an exception to the rule: only 13% of all 2013 cancellations were uploaded in 2013 and the remainder in 2014. As a result, the volume of cancellations in 2013 decreased and the volume of cancellations in 2014 increased sharply (by 127%).
Volume of issued property rights in renewable energy sources (TWh)
Volume of issued cogeneration property rights (TWh)
Volume of cancelled property rights in renewable energy sources (TWh)
Volume of cancelled cogeneration property rights (TWh)
REGISTER OF GUARANTEES OF ORIGIN
Directive 2009/28/EC which imposes the obligation to set up registers of guarantees of origin in the European Union member states was implemented in Poland in an amendment of the Energy Law of 26 July 2013, known as the small energy tripack, effective as of 11 September 2013. It requires PolPX to operate a Register of Guarantees of Origin and to organise trade in guarantees of origin.
In September 2014, PolPX launched the Register of Guarantees of Origin which registers energy from renewable sources and OTC trade in environmental benefits of its production. Unlike certificates of origin, guarantees do not involve property rights or a support system for renewable energy sources: they are issued for information only. There is no obligation to acquire guarantees but they can be used by entities to prove that a certain quantity of consumed energy was generated from renewable sources.
Development plans for the Register of Guarantees of Origin include continuous improvement of the IT system as well as efforts aimed at enabling cross-border transfer of Polish guarantees of origin via AIB Hub, an application which supports communication between national registers.
Since November 2014, PolPX offers trade in guarantees of origin of energy, new support instruments for renewable energy sources which disclose to the final consumer that a given quantity of electricity put into the distribution grid or transmission grid, as stated in the document, was generated from renewable energy sources.
According to the regulations, the Energy Regulatory Office issues guarantees of origin which are then uploaded to the IT system of the Register of Guarantees of Origin operated by PolPX. System users can trade in guarantees of origin or provide them to end users as proof that energy was generated from renewable sources. PolPX can be requested to issue a document confirming for the end customer that the quantity of electricity put into the distribution grid or transmission grid, as stated in the document, was generated from renewable energy sources.
The origin of energy is increasingly important in many EU member states. Guarantees are used to issue certificates which provide details of the source of energy, and companies consider the acquisition of certificates or guarantees to be part of their image strategy. The liquidity of the instrument is supported by the fact that most national registers of guarantees of origin are interconnected via AIB Hub, which supports a free international flow of guarantees.
In view of the current wording of the Energy Law and the wording of provisions concerning guarantees of origin in the draft Renewable Energy Sources Act, Polish guarantees do not meet the formal and legal requirements of participation in the European market. Until the regulations are amended, trade on the market is expected to remain low, especially that Polish companies are less interested than Western companies in acquisition of energy from renewable sources.
CLEARING
The Warsaw Commodity Clearing House (WCCH), which is a subsidiary of PolPX, offers clearing of transactions of PolPX members on its markets.
In 2014, WCCH continued operations launched in 2010 as an exchange clearing house under the Act on Trading in Financial Instruments and the Commodity Exchange Act. Since 2010, WCCH is authorised by the Polish Financial Supervision Authority to clear and settle transactions in financial instruments on the exchange and OTC regulated market.
Currently WCCH clears the full volume of electricity and gas sold on the exchange market in Poland. The total volume of cleared transactions in electricity in 2014 was 186.801 TWh while the total volume of cleared transactions in gas was 111.649 TWh.
Market consensus suggests a steady increase of electricity consumption in Poland and growing interest in exchange trade. The exchange market in gas is growing: the number of market participants is rising and PolPX offers new instruments, which suggests steady further growth of volumes cleared by WCCH. The volume of trading is also driven by the statutory obligation to trade in electricity and gas on an exchange. With its risk management system, WCCH provides competitive clearing services focused on low cost of market participation combined with high safety of trading.
When PolPX launches a financial market, WCCH will be in a position to offer a futures clearing service. The combination of commodity and financial market services available from one provider gives WCCH a major advantage over other clearing houses in the region.
GROWING NUMBER OF POLPX MEMBERS
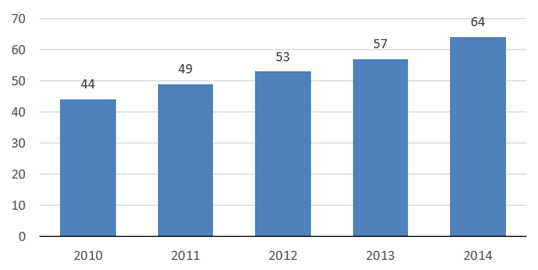
The number of PolPX members is growing steadily, boosting growth of the markets operated by PolPX and their trading volumes. In 2014, PolPX signed agreements with 11 companies and another 7 members joined new markets. At the same time, 5 companies were first authorised to operate on the exchange and 13 members were authorised for individual markets. In 2014, 7 companies terminated their PolPX membership. The figure below presents the number of PolPX members by year in 2010-2014.
Number of PolPX members